새로운 강의는 이제 https://memi.dev 에서 진행합니다.
memi가 Vue & Firebase로 직접 만든 새로운 사이트를 소개합니다.
Flutter와 Firebase로 Android iOS 둘 다 만들기 10 REST API 사용해보기
플러터로 REST API를 시험해봅니다.
개요
파이어베이스 제품군을 이용하면 대부분의 네트워크 및 데이터베이스 상호작용이 가능하지만 외부와의 소통은 REST API가 가장 보편적입니다.
REST 역활을 해줄 간단한 웹서버와 플러터의 http 모듈을 사용해서 테스트해봅니다.
참고: https://flutter-ko.dev/docs/cookbook/networking/fetch-data
웹서버 만들기
기본적으로 nodejs(v10 이상) 와 yarn(v1 이상)이 설치되어 있어야합니다.
프로젝트 생성
$ mkdir koa-rest && koa-rest
$ yarn init
의존요소 설치
웹서버 koa와 도우미 모듈들을 설치합니다.
$ yarn add koa
$ yarn add koa-router
$ yarn add koa-bodyparser
코드 작성
const Koa = require('koa')
const Router = require('koa-router')
const BodyParser = require('koa-bodyparser')
const app = new Koa()
const router = new Router()
app.use(BodyParser())
router
.get('/', (ctx, next) => {
ctx.body = 'get'
})
.post('/', (ctx, next) => {
console.log(ctx.request.body)
ctx.body = 'post'
})
.put('/', (ctx, next) => {
console.log(ctx.request.body)
ctx.body = 'put'
})
.delete('/', (ctx, next) => {
ctx.body = 'delete'
})
app
.use(router.routes())
.use(router.allowedMethods())
app.listen(3000, () => console.log('koa go~'))
간단하게 REST 시험을 해볼 수 있는 코드를 작성해봤습니다.
서버 구동
$ node .
koa go~
서버를 구동시켜 놓고 플러터를 만들러 갑니다.
플러터
REST 고유기능만 확인해보기 위해 새로운 프로젝트로 만들어봅니다.
웹기반에서의 axios 처럼 플러터에도 강력한 http모듈이 있습니다.
모듈 참고: https://pub.dev/packages/http
작업공간 만들기
lib/main.dart
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: RestTest(),
);
}
}
class RestTest extends StatefulWidget {
RestTest({Key key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_RestTestState createState() => _RestTestState();
}
class _RestTestState extends State<RestTest> {
String input = '', response = '';
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Rest test'),
),
body: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
TextField(
onChanged: (t) {
print(t);
input = t;
},
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
Text('post'),
Text('get'),
Text('put'),
Text('delete'),
]
),
Card(
child: Text(response),
)
],
)
),
);
}
}
시험을 진행할 공간을 대충 만들어 둡니다.
http 모듈 설치
pubspec.yaml
dependencies:
##
cupertino_icons: ^0.1.2
http: ^0.12.0+4
http 모듈만 작성하면 vscode에서 자동으로 설치해줍니다.(flutter pub get)
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
상단에 임포트만 해주면 끝입니다.
포스트 해보기
Widget _post () {
return RaisedButton(
child: Text('post'),
onPressed: () async {
const url = 'http://192.168.0.3:3000';
final r = await http.post(url, body: { 'a': input });
print('Response status: ${r.statusCode}');
print('Response body: ${r.body}');
setState(() {
response = r.body;
});
},
);
}
Text(‘post’) 를 post()(_위 코드)로 변경하고 테스트 해봅니다.
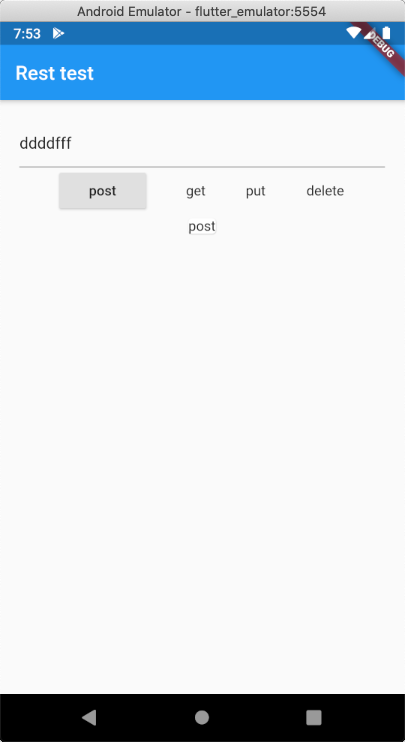
TextField에 적혀있는 값을 보내는 것인데 생각해봐야할 것들이 있습니다.
await http.post(url, body: input)
이렇게 보낼 경우 웹서버에서 바디파서가 json형식이 아니라서 파싱을 정상적으로 못해줍니다.
await http.post(url, body: { 'a': 333 });
333은 String 형식이 아니기 때문에 역시 못보냅니다.
await http.post(url, body: { 'a': 'b', 'c': 'd' });
마치 json 같은 바디의 내용은 사실 json이 아닌 Map<String, String> 형식입니다.
그래서 실제로 적용할 땐 json encode/decode등을 명확하게 이해하고 코드를 작성해야합니다.
json 조립은 다음 강좌에서 진행합니다.
전체 코드
import 'package:flutter/material.dart';
import 'package:http/http.dart' as http;
const url = 'http://192.168.0.3:3000';
void main() => runApp(MyApp());
class MyApp extends StatelessWidget {
// This widget is the root of your application.
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return MaterialApp(
title: 'Flutter Demo',
theme: ThemeData(
primarySwatch: Colors.blue,
),
home: RestTest(),
);
}
}
class RestTest extends StatefulWidget {
RestTest({Key key}) : super(key: key);
@override
_RestTestState createState() => _RestTestState();
}
class _RestTestState extends State<RestTest> {
String input = '', response = 'response!!';
@override
Widget build(BuildContext context) {
return Scaffold(
appBar: AppBar(
title: Text('Rest test'),
),
body: Container(
padding: EdgeInsets.all(20),
child: Column(
children: <Widget>[
TextField(
onChanged: (t) {
print(t);
input = t;
},
),
Row(
mainAxisAlignment: MainAxisAlignment.spaceEvenly,
children: <Widget>[
_post(),
_get(),
_put(),
_delete(),
]
),
Card(
child: Text(response),
)
],
)
),
);
}
Widget _post () {
return RaisedButton(
child: Text('post'),
onPressed: () async {
final r = await http.post(url, body: { 'a': input });
print('Response status: ${r.statusCode}');
print('Response body: ${r.body}');
setState(() {
response = r.body;
});
},
);
}
Widget _get () {
return RaisedButton(
child: Text('get'),
onPressed: () async {
final r = await http.get(url);
print('Response status: ${r.statusCode}');
print('Response body: ${r.body}');
setState(() {
response = r.body;
});
},
);
}
Widget _put () {
return RaisedButton(
child: Text('put'),
onPressed: () async {
final r = await http.put(url, body: { 'a': input });
print('Response status: ${r.statusCode}');
print('Response body: ${r.body}');
setState(() {
response = r.body;
});
},
);
}
Widget _delete () {
return RaisedButton(
child: Text('delete'),
onPressed: () async {
final r = await http.delete(url);
print('Response status: ${r.statusCode}');
print('Response body: ${r.body}');
setState(() {
response = r.body;
});
},
);
}
}
별 내용도 없는데 코드만 깁니다..

댓글남기기